Despite these measures, more intensive acne treatment may be needed, depending on the severity.
Non-medicinal
A first step can be deep cleansing, where comedones are removed with a small needle to reduce inflammation and prevent scarring.
Medicinal
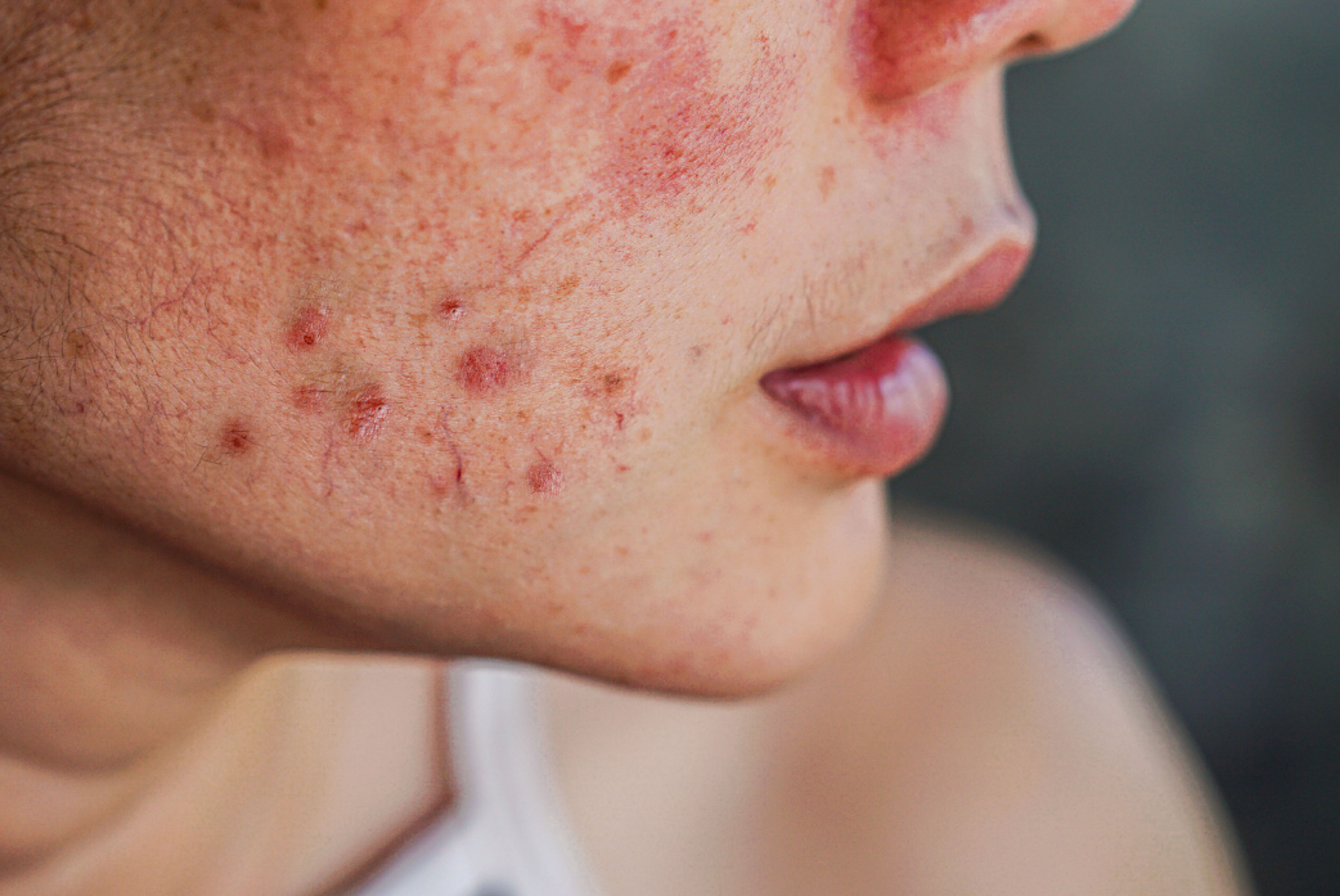
Medicines aim to clear acne quickly, with different treatments for mild, moderate, or severe cases. Mild acne features comedones with minimal inflammation, moderate acne has both comedones and inflammation on the face, while severe acne may involve widespread inflammation, comedones on the torso, or acne conglobata with scarring.
Topical treatments are suitable for mild cases, while moderate to severe acne may require oral medication. Psychological support may also be part of the treatment.
Read the leaflet carefully before starting any medicine. Avoid antibiotics if you have a history of allergic reactions, and complete the prescribed course.
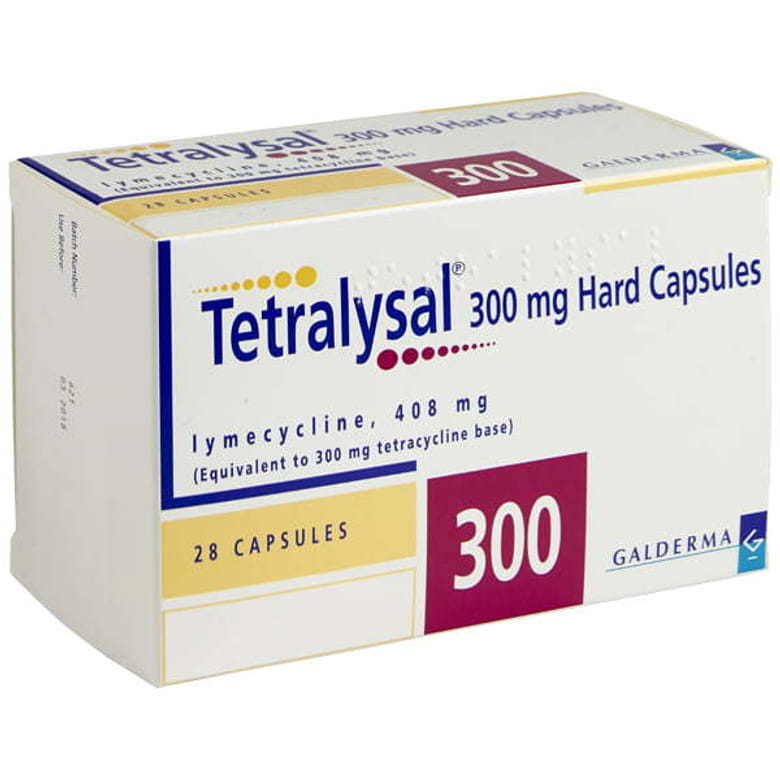
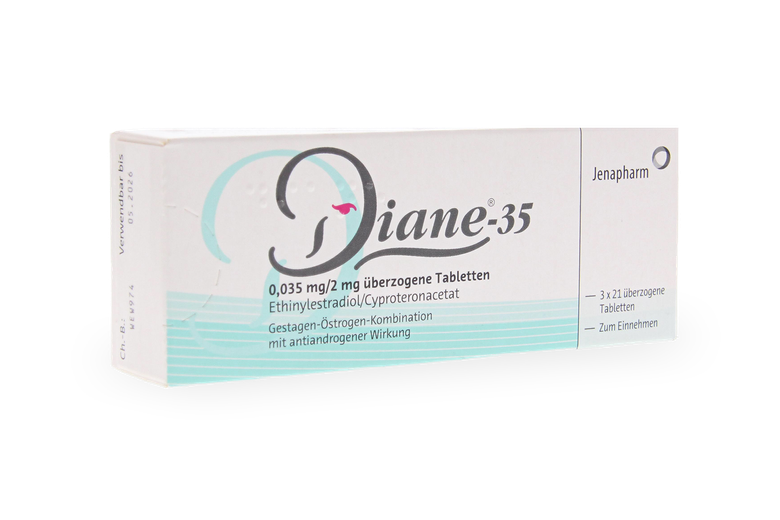
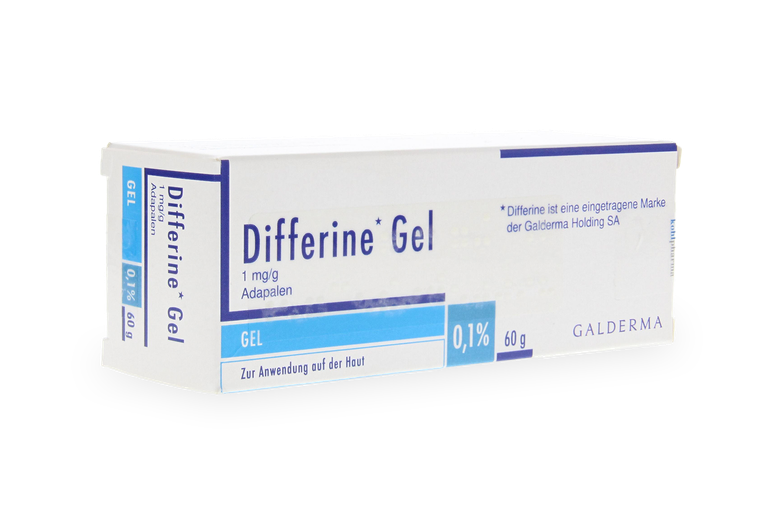
Topical products like benzoyl peroxide gel, adapalene gel, or tretinoin cream help prevent clogged pores. Antibiotics, such as clindamycin or erythromycin, can be applied to the skin or taken orally, and the contraceptive pill may help some women. For moderate cases unresponsive to other treatments, isotretinoin may be considered.
Alternative acne treatments
Microdermabrasion, where the top skin layer is removed, can complement medication to help calm and reduce acne over time.
Acne scars
Acne scars form where the skin heals with different tissue structure, making them visible. Treatments include:
- Chemical peeling: Uses an acidic liquid to remove the top skin layer.
- Laser treatment: Burns off the epidermis in layers.
- Combination treatments: Involving sandblasting, tretinoin cream, and laser to enhance connective tissue.
Psychosocial well-being
Acne can severely affect quality of life, leading to feelings of shame, insecurity, and even depression. If these feelings persist, consult a doctor and consider seeing a psychologist or dermatologist.
Additional risks and side effects
Always read the medication leaflet. Avoid antibiotics if previously allergic, and complete the course.
Potential side effects include:
- Bleaching: Benzoyl peroxide may bleach fabrics, hair, or metal.
- Hyperpigmentation: Skin irritation from benzoyl peroxide or tretinoin increases dark spot risk, especially in darker skin tones.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Avoid acne treatments such as adapalene, tretinoin, clindamycin/tretinoin gel, doxycycline, and isotretinoin during pregnancy or breastfeeding.